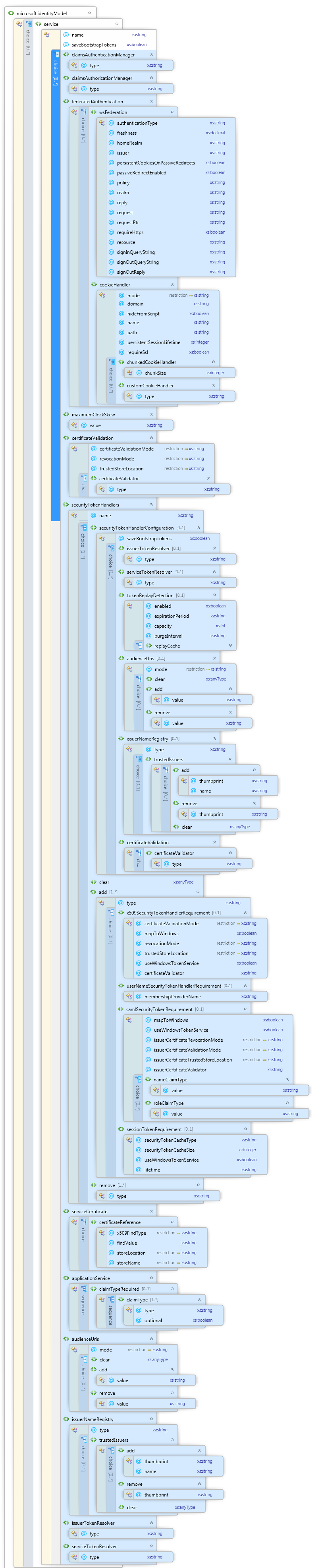
A Hidden Gem: The WIF Config Schema
During the WIF workshops I get various recurring questions: some have open-ended answers which would satisfy my logorrhea but that require A LOT of time to write, others are just a matter a minutes. Today’s post belongs to the latter category.
Some of you would like more detailed documentation about the WIF configuration element: I have discovered that not everybody is aware that the full schema is available in the C:Program Files (x86)Windows Identity Foundation SDKvX.X folder! On top of that, there is also a sample XML file which gives a succinct but super-useful explanation of every element’s usage. I am including here a screenshot of the schema (click for full size!) and I am pasting the sample file, so that you can hit it via search engine if you need to.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <!-- MICROSOFT WINDOWS IDENTITY FOUNDATION ASP.NET RELYING PARTY CONFIGURATION In order to use the Windows Identity Foundation Framework to create an ASP.NET website that acts as a Information Card or WS-Federation relying party, you must make a number of changes to your web.config file. (1) Reference the Microsoft.IdentityModel assembly You must reference the Microsoft.IdentityModel assembly from the system.web/compilation section of your web.config. This section would look like this: <configuration> ... <system.web> ... <compilation> <assemblies> <add assembly="Microsoft.IdentityModel, Version=0.6.1.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35" /> </assemblies> </compilation> ... </system.web> ... </configuration> (2) Register the HTTP module Support for relying party has been built using the following ASP.NET modules. (a) SessionAuthenticationModule (b) WSFederationAuthenticationModule (c) ClaimsPrincipalHttpModule Depending on your scenario you will include one or more of these modules. The below examples show how you must add the WSFederationAuthenticationModule in one of two places depending on your hosting environment. (a) For "classic" ASP.NET (includes IIS6 or IIS7 with a "classic" application pool) You must reference WSFederationAuthenticationModule from the system.web/httpModules section of your web.config. This section would look like this: <configuration> ... <system.web> ... <httpModules> <add name="WSFederatedAuthenticationModule" type="Microsoft.IdentityModel.Web.WSFederatedAuthenticationModule, Microsoft.IdentityModel, Version=0.6.1.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35"/> </httpModules> ... </system.web> ... </configuration> (b) For IIS7 "integrated" mode You must reference WSFederationAuthenticationModule from the system.webServer/modules section of your web.config or applicationHost.config. This section would look like this: <configuration> ... <system.webServer> ... <modules> <add name="WSFederationAuthenticationModule" type="Microsoft.IdentityModel.Web.WSFederationAuthenticationModule, Microsoft.IdentityModel, Version=0.6.1.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35" preCondition="managedHandler"/> </modules> ... </system.webServer> ... </configuration> (3) Register the configuration section In order to use the rest of the configuration described by this file in your web.config, you must reference MicrosoftIdentityModelSection from the configSections section of your web.config. This section would look like this: <configuration> ... <configSections> <section name="microsoft.identityModel" type="Microsoft.IdentityModel.Web.Configuration.MicrosoftIdentityModelSection, Microsoft.IdentityModel, Version=1.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35"/> </configSections> ... </configuration> --> <configuration> <configSections> <!--<section name="microsoft.identityModel" type="Microsoft.IdentityModel.Configuration.MicrosoftIdentityModelSection, Microsoft.IdentityModel, Version=1.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35" />--> <section name="microsoft.identityModel" type="Microsoft.IdentityModel.Configuration.MicrosoftIdentityModelSection, Microsoft.IdentityModel" /> </configSections> <!-- The XML below illustrates the available configuration elements for the WSFederationAuthenticationModule. This section contains some general comments about conventions used throughout. MODES Many of the elements have a 'mode' attribute. This attribute generally controls which class is used to do a particular part of the processing, and which configuration elements are allowed as children of the current element. A configuration error will be raised if elements are included in the configuration file which are ignored because of the mode. TIMESPAN VALUES Where TimeSpan is used as the type of an attribute, see the MSDN documentation for TimeSpan.Parse to see the allowed format, which fits this specification: [ws][-]{ d | [d.]hh:mm[:ss[.ff]] }[ws] For example, "30", "30.00:00", "30.00:00:00" all mean 30 days; and "00:05", "00:05:00", "0.00:05:00.00" all mean five minutes. CERTIFICATE REFERENCES Several elements reference certificates. When referencing a certificate, these attributes are available: storeLocation A value of the System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates.StoreLocation enumeration: CurrentUser, CurrentMachine storeName A value of the System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates.StoreName enumeration; the most useful for this context are: My, TrustedPeople x509FindType A value of the System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates.X509FindType enumeration; the most useful for this context are: FindBySubjectName, FindByThumbprint findValue The value used to find the certificate, based on the x509FindType. To eliminate the chance of error, it is recommended that the FindByThumbprint type be used in production, in which case this attribute has a value which is the hex-string form of the certificate thumbprint; for example, "97249e1a5fa6bee5e515b82111ef524a4c91583f". CUSTOM TYPE REFERENCES Several elements reference custom types, using the 'type' attribute. This attribute should specify the name of the custom type. To reference a type from the GAC, a strong name should be used. To reference a type from an assembly in the bin/ directory, a simple assembly-qualified reference may be used. Types defined in App_Code/ may also be referenced by simply specifying the type name with no qualifying assembly. Custom types must be derived from the type specified, and they must provide a public default (0 argument) constructor. --> <microsoft.identityModel> <!-- Multiple services may be defined, each with a unique name and defining a specific configuration. Example <service name="alternate" > If no name is specified, the service defines the default configuration, which is always used for passive federation scenarios. --> <service> <!-- <securityTokenHandlers> contains the set of SecurityTokenHandlers that are registered with the endpoint. The securityTokenHandlers collection by default is populated with Saml11SecurityTokenHandler, Saml2SecurityTokenHandler, KerberosSecurityTokenHandler, WindowsUserNameSecurityTokenHandler, RsaSecurityTokenHandler, X509SecurityTokenHandler and EncryptedSecurityTokenHandler. Each of the TokenHandler setting can have custom configuration as a child element to the TokenHandler element entry. Saml11SecurityTokenHandler, Saml2SecurityTokenHandler, X509SecurityTokenHandler and MembershipUserNameSecurityTokenHandler have a pre-defined custom configuration section. SecurityTokenHandler collections can also be named, to be used in certain circumstances. The only names that the framework handles are "ActAs" and "OnBehalfOf". If handlers exist in these collections, they will be used lieu of the default handlers for processing ActAs and OnBehalfOf tokens. Example <securityTokenHandlers name="ActAs"> --> <securityTokenHandlers> <!-- Configuration specific to this collection of security token handlers. --> <securityTokenHandlerConfiguration> <!-- <audienceUris> specifies the set of URIs which are acceptable as identifying this relying party. Tokens will not be accepted unless they are scoped for one of the allowed audience URIs. By default, no URIs will be added to the collection. The SecurityTokenHandler for the SAML 1.1 and SAML 2.0 token types use the values in this collection to configure any allowed audience uri restrictions in SamlSecurityTokenRequirement objects. --> <audienceUris> <!-- <clear/> may be used to remove any URIs that may be in this configuration collection. --> <clear/> <!-- Each <add> references an allowed audience URI. --> <add value="http://www.example.com/myapp/" /> <!-- Each <remove> removes an audience URI. --> <remove value="http://www.example.com/myapp/" /> </audienceUris> <!-- issuerNameRegistry - All issuer tokens are validated using the IssuerNameRegistry. The purpose of the IssuerNameRegistry is to map the issuer token to a string name. Any custom type can be registered using the 'type' attribute of the <issuerNameRegistry> element. The <issuerNameRegistry> can have one child element that will serve as custom configuration to the IssuerNameRegistry. One IssuerNameRegistry type is provided out of the box. (a) ConfigurationBasedIssuerNameRegistry - Can be used to configure a set trusted issuer certificates in configuration. This type requires a child configuration element <trustedIssuers> where trusted issuer certificates configured. <trustedIssuers> configuration adds trusted certs using the ASN.1 encoded form of the certificate thumbprint. --> <issuerNameRegistry type="Microsoft.IdentityModel.Tokens.ConfigurationBasedIssuerNameRegistry, Microsoft.IdentityModel"> <trustedIssuers> <add thumbprint="97249e1a5fa6bee5e515b82111ef524a4c9158de" name="contoso.com" /> <remove thumbprint="97249e1a5fa6bee5e515b82111ef524a4c9158de" /> <clear/> </trustedIssuers> </issuerNameRegistry> <!-- <issuerTokenResolver> registers an issuer token resolver. This can be used to resolve Issuer KeyIdentifierClauser while deserializing a SAML token. --> <issuerTokenResolver type="MyNamespace.CustomTokenResolver, MyAssembly" /> <!-- <serviceTokenResolver> registers a service token resolver. This can be used to resolve Issuer KeyIdentifierClauser while deserializing a SAML token. --> <serviceTokenResolver type="MyNamespace.CustomTokenResolver, MyAssembly" /> </securityTokenHandlerConfiguration> <!-- <clear /> may be used to clear all the token handlers in the current collection. --> <clear /> <!-- <remove> can be used to remove a specific TokenHandler from the current collection. ATTRIBUTES type - The CLR type name of the token handler to be removed. --> <remove type="Microsoft.IdentityModel.Tokens.Saml11.Saml11SecurityTokenHandler, Microsoft.IdentityModel" /> <!-- <add> can be used to add a specific TokenHandler from the current collection. The element can be followed by an custom element section. The <add> element can take only one child element which describes the custom configuration. When custom configuration is used the Token Handler type should expose a constructor that takes in an XmlElement. public class CustomTokenHandler : SecurityTokenHandler { public CustomTokenHandler( XmlElement customConfig ) { } } ATTRIBUTES type - The CLR type name of the token handler to be added. --> <add type="MyNamespace.CustomTokenHandler, MyAssembly"> <customConfig myAttr="val"> <customSubConfig> </customSubConfig> </customConfig> </add> <!-- Saml11SecurityTokenHandler and Saml2SecurityTokenHandler have specific custom configuration. This is optional and can be used to change the default settings for any of these. <samlSecurityTokenRequirement> element can appear as child element for a Saml11SecurityTokenHandler or Saml2SecurityTokenHandler or a derived class of any of these. ATTRIBUTES issuerCertificateValidationMode - X509CertificateValidationMode value that specifies the validation mode to use for the X.509 certificate. The default value is PeerOrChainTrust. issuerCertificateRevocationMode - X509CertificateRevocationMode type that specifies the revocation mode to use for the X.509 certificate. The default value is Online. issuerCertificateTrustedStoreLocation - X509TrustedStoreLocation type that specifies the X.509 certificate store. The default value is LocalMachine. issuerCertificateValidator - A custom type that derives from System.IdentityModel.Selectors.X509CertificateValidator. If the certificateValidationMode attribute is "Custom", an instance of this type will be used for issuer certificate validation. mapToWindows - Boolean - Default is false. Specifies whether the token handler should map the validating token to a Windows account by using the incoming UPN claim. useWindowsTokenService - Boolean - Default is false. Specifies whether the token handler should utilize the Windows Token Service to perform the log on operation for the mapToWindows feature. --> <add type="Microsoft.IdentityModel.Tokens.Saml11.Saml11SecurityTokenHandler, Microsoft.IdentityModel"> <samlSecurityTokenRequirement issuerCertificateValidationMode="PeerOrChainTrust" issuerCertificateRevocationMode="Online" issuerCertificateTrustedStoreLocation="LocalMachine" mapToWindows="false" useWindowsTokenService="false"> <!-- <nameClaimType> specifies the claim type that specifies the IIdentity.Name. The value is used to search for a Claim in the SubjectCollection returned by SecurityTokenHandler.ValidateToken and the value of the Claim is set as the name of the IIdentity generated from this token handler. ATTRIBUTES value - URI that specifies the name claim type. --> <nameClaimType value="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/05/identity/claims/name" /> <!-- <roleClaimType> specifies the set of claim type that defines the role type claims in the SubjectCollection created SecurityTokenHandler. ValidateToken. --> <roleClaimType value="schemas.microsoft.com/ws/2006/04/identity/claims/role" /> </samlSecurityTokenRequirement> </add> <!-- MembershipUserNameSecurityTokenHandler has specific custom configuration. <usernameSecurityTokenHandlerRequirement> element can appear as child element for a MembershipUserNameSecurityTokenHandler. membershipProvider- Specifies the MembershipProvider that should be used by this SecurityTokenHandler and must appear as a child element of <usernameSecurityTokenHandlerRequirement> --> <add type="Microsoft.IdentityModel.Tokens.MembershipUserNameSecurityTokenHandler, Microsoft.IdentityModel"> <userNameSecurityTokenHandlerRequirement membershipProviderName="AspNetSqlProvider" /> </add> <!-- X509SecurityTokenHandler has specific custom configuration. <x509SecurityTokenHandlerRequirement> element can appear as child element for a MembershipUserNameSecurityTokenHandler. ATTRIBUTES mapToWindows- boolean value that specifies if the X.509 Certificate being validated should be mapped to a windows account. Default value is false. certificateValidationMode - X509CertificateValidationMode value that specifies the validation mode to use for the X.509 certificate. The default value is PeerOrChainTrust. revocationMode - X509CertificateRevocationMode type that specifies the revocation mode to use for the X.509 certificate. The default value is Online. trustedStoreLocation - X509TrustedStoreLocation type that specifies the X.509 certificate store. The default value is LocalMachine. certificateValidator - A custom type that derives from System.IdentityModel.Selectors.X509CertificateValidator. If the certificateValidationMode attribute is "Custom", an instance of this type will be used by this handler for certificate validation. --> <add type="Microsoft.IdentityModel.Tokens.X509SecurityTokenHandler, Microsoft.IdentityModel"> <x509SecurityTokenHandlerRequirement mapToWindows="true" certificateValidationMode="PeerOrChainTrust" revocationMode="Online" trustedStoreLocation="LocalMachine" useWindowsTokenService="true"/> </add> <!-- <sessionTokenRequirement> element can appear as a child element for a SessionSecurityTokenHandler. ATTRIBUTES lifetime - lifetime of session tokens saveBootstrapTokens - boolean value that specifies if bootstrap tokens should be included int the session token securityTokenCacheSize - Integer - maximum number of entries in the security token cache securityTokenCacheType - String - references a custom type which must be derived from SecurityTokenCache useWindowsTokenService - boolean value that specifies whether WindowsLogon tokens should be mapped to windows accounts --> <add type="Microsoft.IdentityModel.Tokens.SessionSecurityTokenHandler, Microsoft.IdentityModel"> <sessionTokenRequirement securityTokenCacheType="Microsoft.IdentityModel.MruSecurityTokenCache, Microsoft.IdentityModel" saveBootstrapTokens="true" securityTokenCacheSize="500" useWindowsTokenService="false" lifetime="10:00" /> </add> </securityTokenHandlers> <!-- <certificateValidation> controls the settings that token handlers will use to validate certificates, unless those handlers have their own validators set. ATTRIBUTES certificateValidationMode - X509CertificateValidationMode value that specifies the validation mode to use for the X.509 certificate. The default value is PeerOrChainTrust. revocationMode - X509CertificateRevocationMode type that specifies the revocation mode to use for the X.509 certificate. The default value is Online. trustedStoreLocation - X509TrustedStoreLocation type that specifies the X.509 certificate store. The default value is LocalMachine. certificateValidator - A custom type that derives from System.IdentityModel.Selectors.X509CertificateValidator. If the certificateValidationMode attribute is "Custom", an instance of this type will be used by underlying handlers for certificate validation. --> <certificateValidation certificateValidationMode="PeerOrChainTrust" revocationMode="Online" trustedStoreLocation="LocalMachine" > <!-- <certificateValidator> allows for a custom type to be specified for certificate validation. This type will only be used if the certificateValidationMode is set to "Custom" Type - A custom type that derives from System.IdentityModel.Selectors.X509CertificateValidator. This validator will be used by the default SecurityTokenHandler instances, unless those have their own validators set. --> <certificateValidator type="CustomType" /> </certificateValidation> <!-- <maximumClockSkew> Controls the maximum allowed clock skew when performing time-sensitive operations such as validating the expiration time of a sign-in session. Defaults to 5 minutes. --> <maximumClockSkew value="00:05:00" /> <!-- <serviceCertificate> controls the certificate used for token decryption. In the case of an Information Card relying party, this should be the SSL certificate of the web site. Any certificate that is identified must have a private key and the private key must have appropriate access control permissions so that it may be read by the application pool identity. --> <serviceCertificate> <!-- <certificateReference>, See the comments before the <configuration> element on certificate references. --> <certificateReference x509FindType="FindByThumbprint" findValue="97249e1a5fa6bee5e515b82111ef524a4c91583f" storeLocation="LocalMachine" storeName="My" /> </serviceCertificate> <!-- <federatedAuthentication> contains all the settings used by the ASP.NET modules. ATTRIBUTES enabled - Boolean - default false Controls whether the module added to the ASP.NET pipeline is enabled so that it actively processes each request. The specfic task each module might do depends on the module that is added in the pipeline. --> <federatedAuthentication> <!-- <wsFederattion> defines parameter settings for WS-FEDERATION protocol STS. This affects the settings for the WSFederationAuthenticationModule. ATTRIBUTES Parameters for WS-Federation authenticationType - String - default "" The request wauth type freshness - Float - default "" The value of the required freshness. homeRealm - String - default "" The home realm of the IdentityProvider issuer - String - default "" The URI of the token issuer. policy - String - default "" The URI of the relevant policy. realm - String - default "" The URI of requesting realm. reply - String - default "" The URI of address to reply to. request - String - default "" The URI of WS-FEDERATION request. requestPtr - String - default "" The URI of WS-FEDERATION request pointer. resource - String - default "" The URI of WS-FEDERATION resource value. requireHttps - Boolean - default true Controls whether the module will only redirect a secure URL for the STS. passiveRedirectEnabled - Boolean - default false Controls whether the module is enabled to automatically redirect unauthorized requests to an STS. persistentCookiesOnPassiveRedirects - Boolean - default false Specifies whether persistent cookies are issued when the module is enabled to initiate WS-Federation passive protocol redirects. signInQueryString - String - default "" Application defined parameters for the sign in request URL signOutQueryString - String - default "" Application defined parameters for the sign out request URL signOutReply - String - default "" URL to return to following sign out. --> <wsFederation authenticationType="wauth" freshness="45" homeRealm="http://homeRealm" issuer="i" policy="http://policy" realm="http://realm" reply="http://reply" request="http://request" requestPtr="http://requestPtr" resource ="http://resource" requireHttps="true" passiveRedirectEnabled="true" persistentCookiesOnPassiveRedirects="true" signInQueryString="abc=xyz" signOutQueryString="def=uvw" signOutReply="http://signoutreply" /> <!-- <cookieHandler> controls the CookieHandler, which is responsible for reading and writing raw cookies at the HTTP protocol level. SessionAuthenticationModule uses the cookieHandler to read and write cookies. MODES Default (default) The same as Chunked. Chunked Uses an instance of the ChunkedCookieHandler class. This cookie handler ensures that individual cookies do not exceed a set maximum size. It accomplishes that by potentially "chunking" one logical cookie into a number of on-the-wire cookies. Custom Uses an instance of a custom CookieHandler-derived class, referenced by the <customCookieHandler> element. ATTRIBUTES domain - String - default "" The domain value for any cookies written. hideFromScript - Boolean - default true Controls whether the "HttpOnly" flag is emitted for any cookies written. Certain web browsers honor this flag by keeping client-side script from accessing the cookie value. name - String - default "FedAuth" Controls the base name for any cookies written. path - String - default is HttpRuntime.AppDomainAppVirtualPath Controls the path value for any cookies written. requireSsl - Boolean - default false Controls whether the "Secure" flag is emitted for any cookies written. If this value is set, the sign-in session cookies will only be available over HTTPS. --> <cookieHandler mode="Custom" domain=".example.com" hideFromScript="true" name="FedAuth" path="/" requireSsl="true" persistentSessionLifetime="60"> <!-- <chunkedCookieHandler> may only be present if the cookieHandler/@mode is Default or Chunked. It controls the ChunkedCookieHandler. ATTRIBUTES chunkSize - Int32 - default 2000 The maximum size in characters of the HTTP cookie data for any one HTTP cookie. Care must be taken when adjusting the chunk size. Web browsers have different limits on the size of cookies and number per domain. The original Netscape specification stipulated these limits: 300 cookies total, 4096 bytes per cookie header (including metadata, not just the cookie value), and 20 cookies per domain. --> <chunkedCookieHandler chunkSize="2000" /> <!-- <customCookieHandler> may only be present if the cookieManager/@mode is Custom. It references a custom type which must be derived from CookieHandler. See the comments before the <configuration> element on custom type references. --> <customCookieHandler type="MyNamespace.CustomCookieHandler, MyAssembly" /> </cookieHandler> </federatedAuthentication> <!-- claimsAuthenticationManager - Registers a Authentication Manager for the incoming claims. ClaimsAuthenticationManager that echos the incoming claims is provided through SimpleClaimsAuthenticationManager. <claimsAuthenticationManager> element can be used to register other custom types as well. The element does not provide mechanism to add any custom configuration for the defined types. --> <claimsAuthenticationManager type="MyNamespace.CustomClaimsAuthenticationManager, MyAssembly"/> <!-- claimsAuthorizationManager - Registers a Authorization Manager for the incoming claims. --> <claimsAuthorizationManager type="MyNamespace.CustomClaimsAuthenticationManager, MyAssembly"/> </service> </microsoft.identityModel> </configuration>